Blood clotting is a physiological process that avoids excessive
bleeding during injury. In short, it is a process of thinking of blood. During
injury, the process of blood clotting works to stop bleeding.
When we think about its benefits, it is the best process. Blood clotting stops injury to be prolonged. On the other hand, it may be a dangerous process. When the clots do not dissolve themselves they cause blockage.
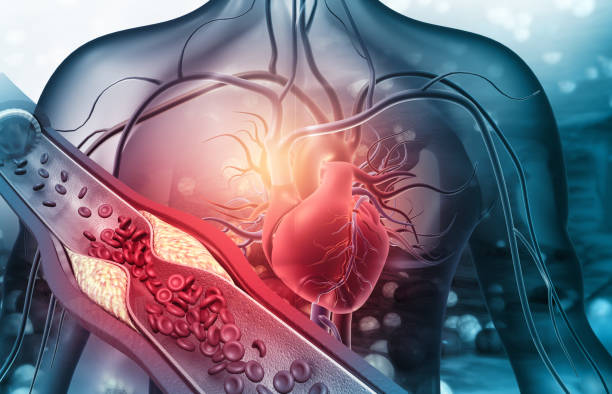
The blockage due to the clot formation causes serious issues such as heart attack. Blood clotting is also known as coagulation. It occurs in response to the injury.
What is a blood clot?
A blood clot is a mass having gel-like consistency. It is formed at the place of injury by the action of platelets and fibrin. The purpose of blood clotting is to stop bleeding.
It may be a dangerous process when the clot
forms within the vessels and cause blockage.
Risk factors of blood clotting
Blood clotting or coagulation can occur in abnormal conditions. Here are some risk factors that can cause blood clotting.
· State of long term immobility
· Smoking
· Use of birth control pills
· Any kind of surgery, especially orthopedic surgery.
· High blood pressure
· High level of cholesterol
· Diabetes
· Internal injury
Causes of
blood clotting
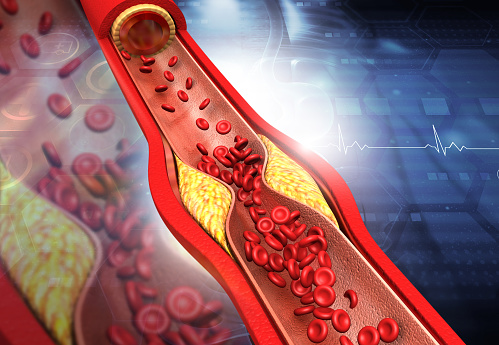
Coagulation or blood clotting have multiple
causes. If it is due to some injury, it is normal. If it occurs due to
abnormalities it leads to severe health issues. Some common causes are:
·
Prolonged immobility:
Our body is made up of several structures. Any immobility causes blood to slow down. The process of blood clotting initiates. The loss of mobility may be due to work purpose or some injury.
· Smoking:
Smokers are more prone to blood clotting. It causes thickening of the blood which results in coagulation.
·
Obesity
Obesity is the mother of diseases. It causes the thickness of the blood.
·
Family History
Some diseases run from one generation to the next. Blood clotting may also have a family background. If you have a family history you should take preventive steps.
Other causes of blood clotting are:
· Pregnancy
· Trauma
· Birth Control pills
· Aging
· Autoimmune diseases
· Chorionic infection
· AIDs or HIV
Types of
blood clots:
There are two types of blood clotting.
· Thrombus:
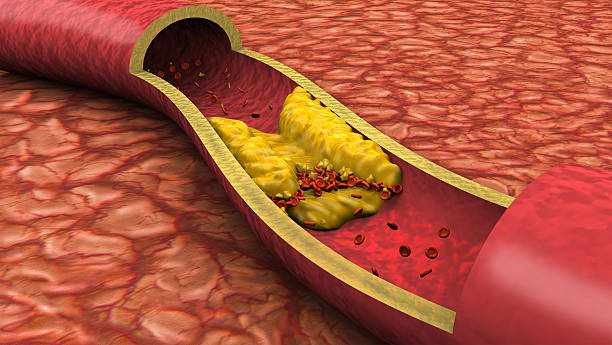
In this type, the clot remains stationary. That means it remains in its
position. It does not flow in the direction of blood. It blocks the passage of
blood and results in serious issues.
· Embolus:
In this type, the clot is movable. These are very dangerous because they can move to the other part of the body. If they reach the heart, they result in heart issues.
Symptoms of blood clotting
Symptoms of coagulation vary depending upon the area of clotting. Coagulation may occur in the legs, arms, abdomen, and heart.
Symptoms depend upon the type of blood
clotting.
· Arm and legs:
The area of the clot becomes red and warm. Swelling occurs. The patient experiences pain and cramps. The infected Arm shows a clear difference.
· Abdominal clot
Abdominal blood clotting results in serious pain in the stomach. Symptoms also include diarrhea and vomiting.
· Heart
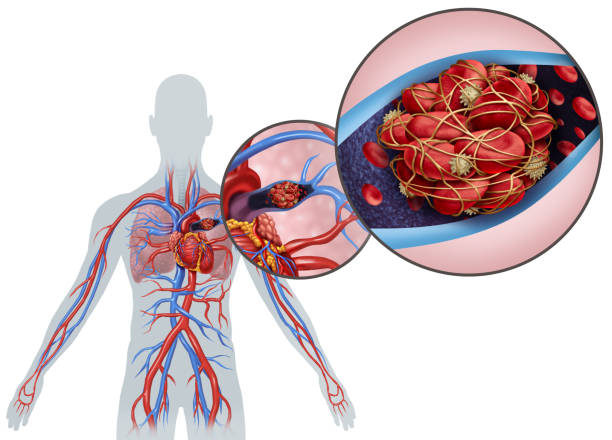
The symptoms include difficulty breathing. The patient suffers from heavy pain in the chest. In addition to nausea, more sweating results.
· Clot in lungs
The symptoms of coagulation in the lungs include severe pain in the chest. The patient experiences blood in the cough. Fever and sweating may involve.
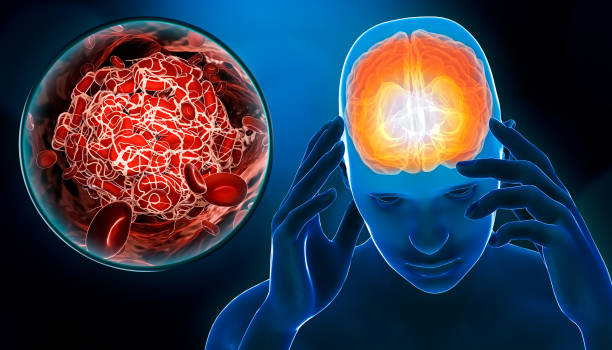
· Clotting in brain
Blood
clotting in the brain includes headaches and dizziness. The patient will unable
to see and talk clearly. Weakness results.
Coagulation also has further classification.
There may be
· Arterial blood clotting
· Venous blood clotting
Arterial blood clotting
Coagulation occurs in the arteries. Arteries transport blood with oxygen to the body. Any blockage in arteries breaks the blood supply to the organs. This leads to tissue death.
Symptoms of arterial blood clotting
Symptoms appear as the clot develops and becomes large. These are:
· Cold in arm or legs
· Loss of color of the affected part
· Muscular pain in the affected area
· Weakness of the affected part
Venous blood
clotting
It is the coagulation in veins. Veins are responsible for blood supply to the heart from the whole body. Venous coagulation is of three types
· Superficial venous thrombosis
Coagulation occurs in the veins that are closer to the skin. This kind of thrombus remains in its place. As it reasons for the pain, it needs treatment.
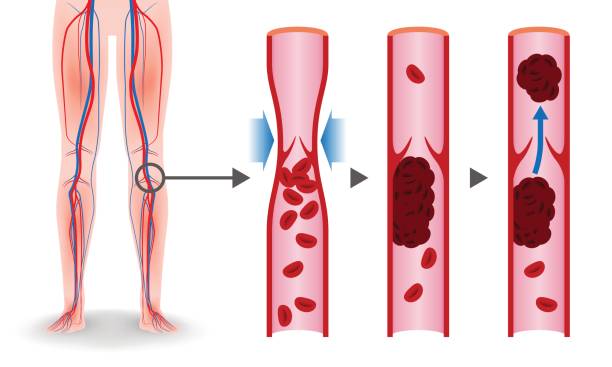
· Deep vein thrombosis
Blood clotting occurs in the deep veins. It affects the major veins of our body because they are deep. In most common conditions, it affects the legs and thigh. It can also develop in the brain or kidneys.
· Pulmonary embolism
It is a very
severe condition. In this situation, the thumbs cut off from their place of
development. It moves and reaches the lungs. This type of blood clotting may be
fatal.
Symptoms of
venous blood coagulation
In superficial vein thrombosis patients suffer from:
· Pain
· Inflammation
· Swelling of the affected part
· Redness
In the case of deep vein thrombosis symptoms are:
- The affected leg undergoes swelling
- Warm and red skin·
- \ Severe pain on movement
In serious conditions when it reaches the lungs patient experiences:
· Difficulty in breathing
· Pain in the chest
· Rapid heart beating
· Cough with blood
· Pain in different parts of the body such as in the legs and shoulders.
Diagnosis of
blood clotting
We have to perform different tests to find the cause and type of blood clotting. All diagnostic procedure includes:
· Blood test
The doctor recommends a blood test to detect the presence of coagulation.
· Ultrasound
It is best to detect the blockage in arteries or veins.
· CT scan
Scan of different parts of the body detects the presence of coagulation. The doctor may ask for a scan of the heart, abdomen, or kidney.
· Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
In serious conditions, MRI is best to determine the process of blood clotting.
Treatment
The tests detect the type of coagulation. Treatment also depends upon the test reports.
Medication
The doctor prescribes Anticoagulants. These are also called blood thinners.
Surgery
It is on the cause and type of coagulation. When it is difficult to treat blood clotting with medication, surgery becomes important.
Stents
The doctor may add stunts to open the blood vessels. It prevents blood clotting in the future.
Comments
Post a Comment